(3) Concrete Column Footing:
Column footing may be isolated (for single column) or combined (for more than one column) It is made up of reinforced cement concrete and hence called RCC footing, RCC footing is used for columns and walls carrying heavy loads or at the places where the hearing capacity of the soil is low. This footing can be square, rectangular or circular. It may be of uniform thickness or sloped as shown in Fig. 2.5. This type of footing is constructed over an 80 mm thick layer of lean concrete. The minimum thickness of RCC footing is 150 mm Reinforcement in the form of bars is placed near the bottom face of the footing in both directions as shown in Fig. 2.5.
 |
| Fig 2.5 R.C.C Foundation. |
(4) Inverted Arch Footing:
Inverted arch footing is used in bridges, reservoirs, or support for drainage lines. It is not used in buildings. This footing provides a larger area for the distribution of superstructure load to the soil as shown in Fig. 2.6.
 |
| Fig. 2.6 Inverted Arch Foundation. |
In this type of footing, special attention is given to strengthening the end pier by constructing a buttress that can counter the horizontal thrust transmitted by the end arch to the end pier. Inverted arch footing has the advantage that the depth of foundation is greatly reduced, especially in the case of soft soils. These footings are not used nowadays because of their skilled construction.
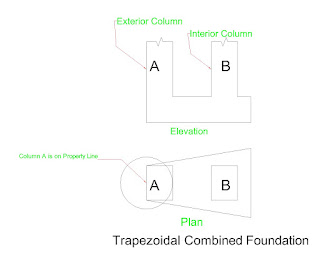
2.4.2. Combined Footing:
A combined footing is provided for two or more columns together under the
following circumstances:
1. When
one of the columns is located near the property line and the individual
footings of the columns may extend outside the property line.
2. When
the individual footings of the columns overlap each other due to proximity.
3. When
the required area of an individual footing is more due to low bearing capacity
of the soil.
This footing maybe rectangular if the two columns carry equal loads and trapezoidal if columns carry unequal loads as shown in Fig. 2.7.
 |
2.4.3. Raft Foundation:
It is a type of shallow foundation which is most suitable for heavy structures to be built on soft and marshy soil types which can cause differential settlement of the building. The Raft foundation consists of R.C.C slab covering the entire area or a slab with beams above it. It is also known as mat foundation because RCC slab covers the entire area under the structure like a mat. It is similar to an inverted beam and slab system. Raft foundation also provides a very wide area for dispersion of structural load thus reducing the intensity of pressure considerably. This results in a reduction in the overall settlement of the building.
2.4.4. Grillage Foundation:
This type of foundation is used only when the loads are very heavy and the soil is poor Let suppose. the bearing capacity of the soil is very low. This type of footing is much lighter and does not require deep excavation. Based upon the type of material used, the grillage foundation is of the following two types:
2.4.4.1. Steel Grillage Foundation:
This
type of foundation consists of rolled steel joists or steel beam embedded in
the cement concrete. The rolled steel joists (RSJ), known as grillage beams,
maybe provided in one tier or two tiers depending upon the intensity of load
to be transferred. The depth of this foundation is limited to 1 to 15 m. This
type of foundation is constructed as follows:
(a) The foundation is excavated to the required depth, the soil is rammed and compacted
well.
(b) A
concrete bed of 150 mm thickness is laid and compacted well.
(c) When
the concrete bed is hardened then the first tier of grillage beams is put on
the bed using spacer bars to keep the beams in position.
(d) Now the second tier of beams is put over the first tier but at right angles to the
first tier.
(e) The entire space is now concreted with a minimum cover of 100 mm on all the sides of the beams.
Figure 2.9 shows a steel grillage foundation for a steel stanchion.
2.4.4.2. Timber Grillage Foundation:
This type of foundation
is used for soils and timber beams. This type of foundation is used for soils
that always remain water-logged. It consists of timber planks and timber
beams. This type of foundation is constructed on a timber platform rather than
a concrete block. The timber platform is made up of timber planks of 50 mm to
80 mm in thickness, placed side by side. Timber beams of size 100 mm x 120 mm
are placed over the timber platform covering its full length and breadth. A
heavy log of suitable dimension is placed in the center over the timber beams
and the timber column is constructed above this log. The load transfer path for
such a footing is as follows:
Deep Foundations
Introduction:
The foundations that are constructed sufficiently below the ground level are called deep foundations. The depth of the deep foundation is very large as compared to its width. Deep foundations are required to be constructed in any of the following conditions:
1. The bearing capacity of topsoil is very poor and the strata of good bearing capacity deep. So the foundation has to be taken deep into the ground and unevenly distributed.
2. The structural load is heavy and unevenly distributed.
3. For structures constructed on the seashore or river bed (bridge piers), where there is the possibility of scouring action of water. In these cases, the foundation must be placed below the scouring depth, even if the suitable bearing stratum is available at shallow depth.
4. If the underground water level is high or fluctuating and it is difficult or uneconomical to pump the water from the open trenches of the shallow foundation.
Deep foundations are of the following types:
(a) Pile foundation
(b) Pier foundation.
(c) Caisson or well foundation.













0 comments:
Post a Comment